Digital Divide
Digital Divide Study Guide
AP Computer Science Principles - Big Idea 5
An illustration showing the digital divide with people on opposite sides of a technological gap
What is the Digital Divide?
Key Dimensions of the Digital Divide:
- Access divide: Physical access to technology and internet
- Usage divide: Skills and capabilities to use technology effectively
- Quality divide: Differences in connection speed, reliability, and devices
- Participation divide: Ability to contribute to and benefit from digital resources
Digital Divide Statistics to Know
Global Internet Access Visualization
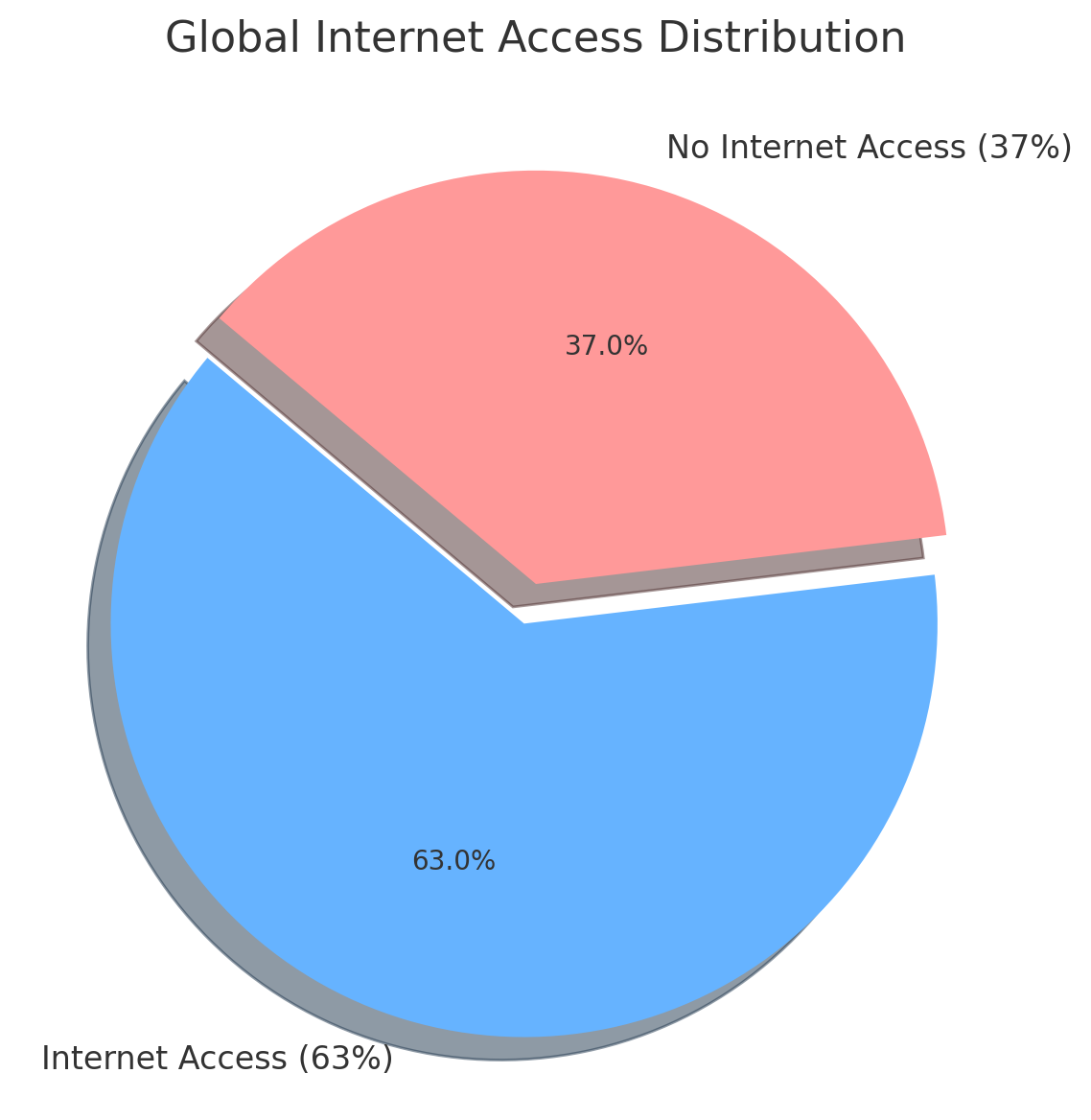
Key Statistics:
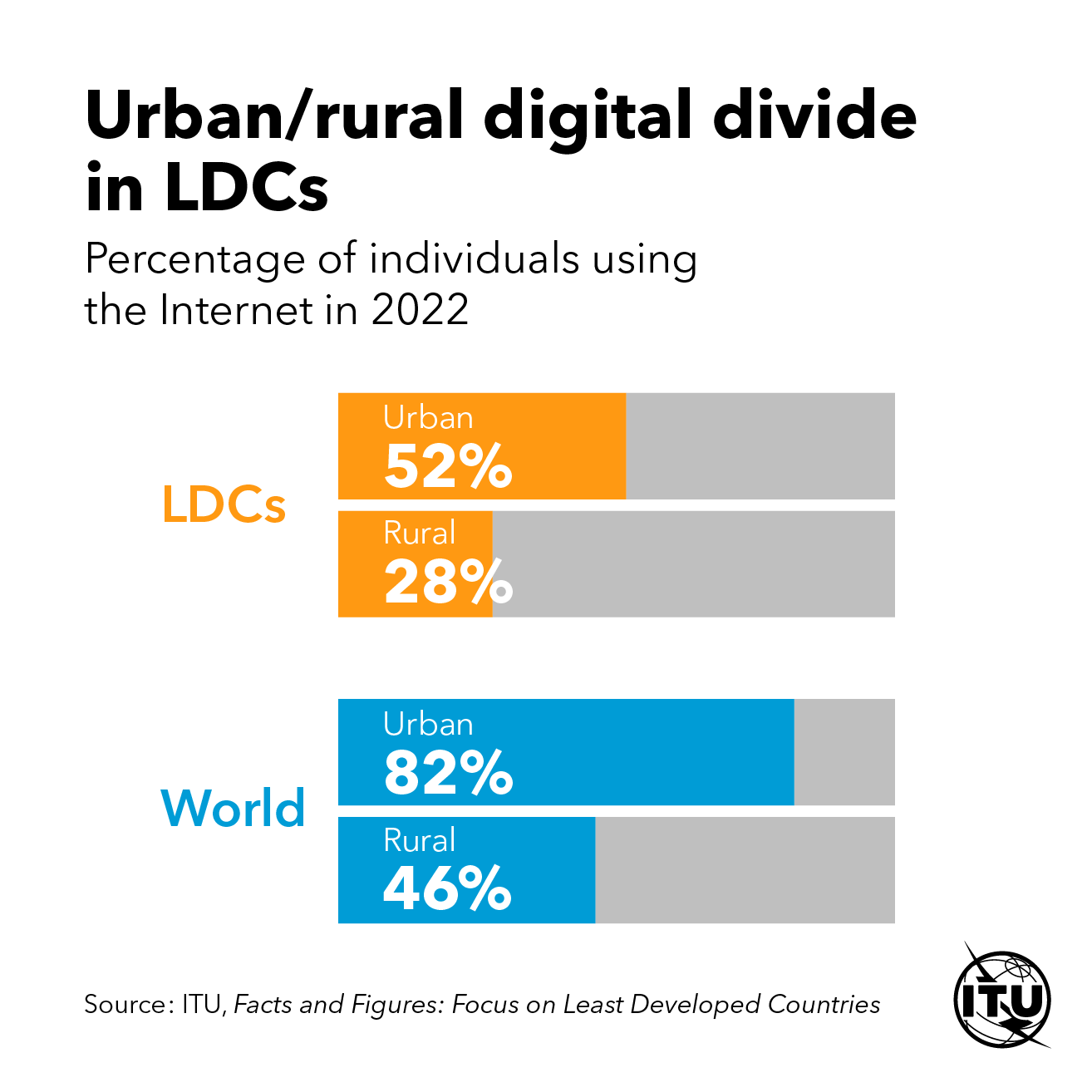
- Rural vs Urban Divide:
- Rural Africa: 22% connectivity rate
- Urban Africa: 76% connectivity rate
- Regional Disparities:
- Northern Europe: 95%+ connectivity
- Central Africa: under 30% connectivity
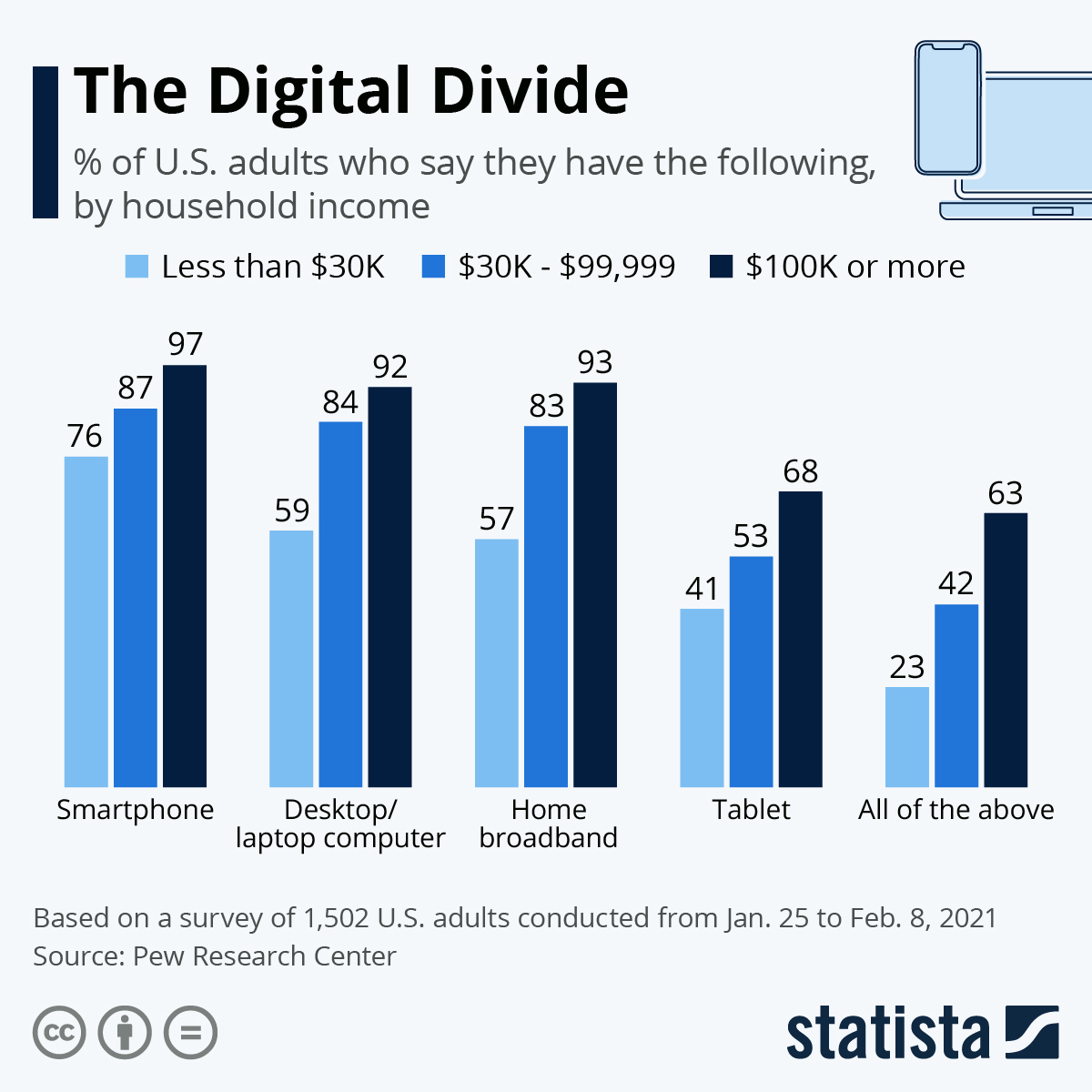
- U.S. Disparities:
- Urban: 94% broadband access
- Rural: 83% broadband access
- High-income households: 95% internet access
- Low-income households: 67% internet access
- Age 18-29: 97% use internet
- Age 65+: 61% use internet
📊 Interactive Activity: Explore the Data
Try this interactive code to visualize different aspects of the digital divide:
// Interactive Digital Divide Explorer
function exploreDigitalDivide() {
// Select what data to display
const metric = prompt(
"Which digital divide metric would you like to explore?\n" +
"1: Income-based internet access\n" +
"2: Urban vs rural access\n" +
"3: Age-based internet usage\n" +
"4: Global connectivity rates"
);
// Sample data
const incomeData = {
categories: ["Lowest 20%", "Second 20%", "Middle 20%", "Fourth 20%", "Highest 20%"],
values: [62, 71, 80, 88, 95]
};
const locationData = {
categories: ["Urban", "Rural"],
values: [94, 83]
};
const ageData = {
categories: ["18-29", "30-49", "50-64", "65+"],
values: [97, 93, 88, 61]
};
const globalData = {
categories: ["North America", "Europe", "Asia Pacific", "Latin America", "Middle East/Africa"],
values: [90, 87, 54, 68, 40]
};
// Select dataset based on user choice
let data;
let title;
switch(metric) {
case "1":
data = incomeData;
title = "Internet Access by Income Level (%)";
break;
case "2":
data = locationData;
title = "Urban vs Rural Internet Access (%)";
break;
case "3":
data = ageData;
title = "Internet Usage by Age Group (%)";
break;
case "4":
data = globalData;
title = "Internet Access by Region (%)";
break;
default:
alert("Invalid selection!");
return;
}
// Display the data (in a real app, this would create a chart)
console.log(title);
console.log("=".repeat(title.length));
const maxValue = Math.max(...data.values);
const maxBarLength = 40;
for (let i = 0; i < data.categories.length; i++) {
const barLength = Math.round((data.values[i] / maxValue) * maxBarLength);
const bar = "█".repeat(barLength);
console.log(`${data.categories[i].padEnd(12)}: ${bar} ${data.values[i]}%`);
}
}
// Run this function to explore different aspects of the digital divide
// exploreDigitalDivide();
Try it yourself! Copy this code into a JavaScript console and run the exploreDigitalDivide() function to visualize different aspects of the digital divide.
Factors Contributing to the Digital Divide
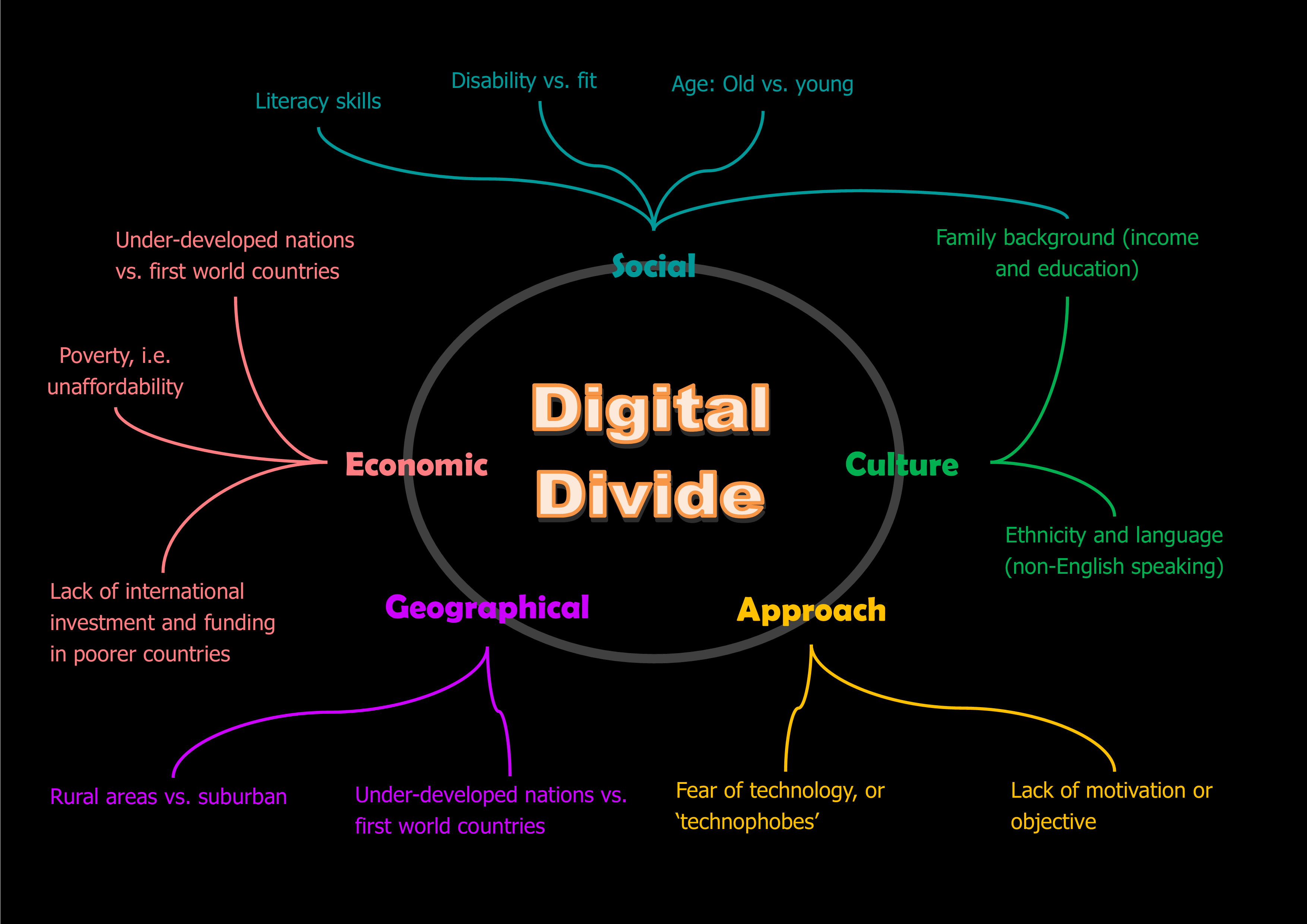
Economic Factors
- Cost of devices
- Subscription fees
- Maintenance expenses
- Affordability relative to income
Infrastructure
- Availability of broadband networks
- Cellular coverage
- Fiber optic deployments
- Electricity reliability
Geography
- Urban vs. rural locations
- Terrain challenges (mountains, remote islands)
- Population density
- Distance from connection points
Education and Skills
- Digital literacy levels
- Technical knowledge
- Language barriers
- Educational opportunities
Policy and Governance
- Government initiatives
- Regulatory frameworks
- Investment priorities
- Universal service programs
Social and Cultural Factors
- Age differences
- Disability access
- Language barriers
- Cultural attitudes toward technology
- Gender disparities
🎮 Game: “Bridge the Divide” Challenge
Test your understanding of the digital divide with this text-based mini-game:
// Bridge the Divide Challenge Game
function bridgeTheDivideGame() {
console.log("===============================================");
console.log("🌉 BRIDGE THE DIVIDE: Digital Inclusion Challenge");
console.log("===============================================");
console.log("You are a technology policy advisor tasked with");
console.log("helping communities overcome the digital divide.");
console.log("Analyze each scenario and make the best decision!\n");
let score = 0;
const totalQuestions = 5;
// Scenario 1
console.log("SCENARIO 1: Rural Connectivity");
console.log("A rural community of 500 families is located 50 miles from");
console.log("the nearest broadband infrastructure. You have $200,000");
console.log("in funding. What's your best approach?");
console.log("A: Lay fiber optic cable to each home");
console.log("B: Set up a wireless tower system");
console.log("C: Provide satellite internet subsidies");
console.log("D: Create a community center with high-speed internet");
const answer1 = prompt("Your choice (A/B/C/D):").toUpperCase();
if (answer1 === "B") {
console.log("✓ Correct! A wireless tower system provides the best");
console.log(" coverage for the investment in this rural setting.");
score++;
} else {
console.log("✗ The best answer is B. Fiber would be too expensive,");
console.log(" satellite has high latency issues, and a single center");
console.log(" wouldn't provide sufficient access for all families.");
}
// Scenario 2
console.log("\nSCENARIO 2: Digital Literacy");
console.log("An urban neighborhood has new affordable internet access,");
console.log("but adoption remains low at 30%. Investigation reveals many");
console.log("residents lack digital skills. What approach would help most?");
console.log("A: Reduce internet prices further");
console.log("B: Distribute free tablets to all residents");
console.log("C: Launch digital literacy workshops at local library");
console.log("D: Create a tech support hotline");
const answer2 = prompt("Your choice (A/B/C/D):").toUpperCase();
if (answer2 === "C") {
console.log("✓ Correct! Digital literacy workshops address the");
console.log(" root cause - lack of skills - rather than just");
console.log(" providing more access or support.");
score++;
} else {
console.log("✗ The best answer is C. The primary barrier isn't");
console.log(" cost or device ownership, but skill development.");
console.log(" Workshops provide hands-on learning opportunities.");
}
// Add more scenarios as needed...
// Final score
console.log("\n===============================================");
console.log(`FINAL SCORE: ${score}/${totalQuestions}`);
console.log("===============================================");
if (score === totalQuestions) {
console.log("🏆 Perfect! You're a digital inclusion expert!");
} else if (score >= totalQuestions * 0.7) {
console.log("🥈 Good job! You have strong understanding of digital divide issues.");
} else if (score >= totalQuestions * 0.5) {
console.log("👍 Decent effort, but review some of the concepts again.");
} else {
console.log("📚 You need more study on digital divide solutions.");
}
}
// Run the game with: bridgeTheDivideGame();
Challenge yourself! Run this function in a JavaScript console to test your knowledge of digital divide solutions.
Impacts of the Digital Divide
Economic Impacts
- Limited job opportunities
- Reduced business prospects
- Innovation barriers
- Lower earning potential
Educational Impacts
- Limited access to learning resources
- Reduced skill development
- Homework gap
- Restricted career preparation
Social Impacts
- Decreased civic participation
- Limited access to government services
- Health information disparities
- Social isolation
Health Impacts
- Restricted telehealth access
- Limited health information
- Fewer healthcare options
- Challenges with appointment scheduling
📱 Case Study: COVID-19 Pandemic

The pandemic highlighted and exacerbated existing digital divides:
- Remote learning challenges: Students without reliable internet or devices fell behind
- Telehealth limitations: Those without digital access struggled to receive medical care
- Work from home disparities: Jobs requiring digital presence became inaccessible
- Vaccine appointment scheduling: Digital-first systems created barriers
- Government services: Online benefits systems excluded many without access
Solutions to Bridge the Digital Divide
🛠️ Interactive Solution Explorer
// Digital Divide Solution Explorer
function solutionExplorer() {
const problemType = prompt(
"What type of digital divide problem are you trying to solve?\n" +
"1: Access (physical availability)\n" +
"2: Affordability\n" +
"3: Digital literacy\n" +
"4: Accessibility (for people with disabilities)"
);
const context = prompt(
"What is the context?\n" +
"1: Urban area\n" +
"2: Rural area\n" +
"3: School/Education\n" +
"4: Senior citizens"
);
const resources = prompt(
"What resources are available?\n" +
"1: Limited budget\n" +
"2: Moderate funding\n" +
"3: Community partners\n" +
"4: Technical expertise"
);
// Generate recommendations based on inputs
console.log("\n📋 RECOMMENDED SOLUTIONS:\n");
// Access solutions
if (problemType === "1") {
if (context === "1") { // Urban + Access
console.log("• Establish public WiFi networks in community spaces");
console.log("• Partner with local businesses to create 'connected corridors'");
console.log("• Implement device lending programs through libraries");
} else if (context === "2") { // Rural + Access
console.log("• Deploy fixed wireless solutions");
console.log("• Explore satellite internet subsidies");
console.log("• Create community hub with high-speed connection");
}
// More combinations...
}
// Affordability solutions
if (problemType === "2") {
console.log("• Develop tiered pricing based on income");
console.log("• Create subsidy programs for low-income residents");
console.log("• Implement refurbished device distribution");
// Context-specific solutions...
}
// Digital literacy solutions
if (problemType === "3") {
if (context === "4") { // Seniors + Digital Literacy
console.log("• Design age-appropriate training workshops");
console.log("• Create peer mentor programs with tech-savvy seniors");
console.log("• Develop simplified interface tools");
} else {
console.log("• Establish regular training workshops");
console.log("• Create easy-to-follow tutorial materials");
console.log("• Implement buddy systems for ongoing support");
}
// More combinations...
}
// Accessibility solutions
if (problemType === "4") {
console.log("• Promote accessible design standards");
console.log("• Provide assistive technology");
console.log("• Develop specialized training programs");
// Context-specific solutions...
}
console.log("\n💡 IMPLEMENTATION TIPS:");
if (resources === "1") { // Limited budget
console.log("• Start with a small pilot program");
console.log("• Focus on highest-need populations first");
console.log("• Seek volunteer technical support");
} else if (resources === "3") { // Community partners
console.log("• Create a multi-stakeholder working group");
console.log("• Divide responsibilities among partners");
console.log("• Leverage existing community relationships");
}
// More resource combinations...
}
// Try it with: solutionExplorer();
Try this interactive tool! It will recommend solutions based on the specific digital divide challenge you’re trying to address.
Technological Solutions
- Low-cost devices (Chromebooks, Raspberry Pi)
- Mesh networks
- Mobile-first design
- Offline capabilities
- Alternative connection methods (satellite internet, community networks)
- Solar-powered internet kiosks
Policy Solutions
- Universal service programs
- Digital literacy initiatives
- Public access points (libraries, community centers)
- Subsidized internet for low-income households
- Rural broadband expansion initiatives
- Technology recycling programs
Social Solutions
- Community tech centers
- Peer-to-peer teaching
- Device donation programs
- Multi-language content development
- Accessible design practices
- Intergenerational technology programs
Real-World Examples
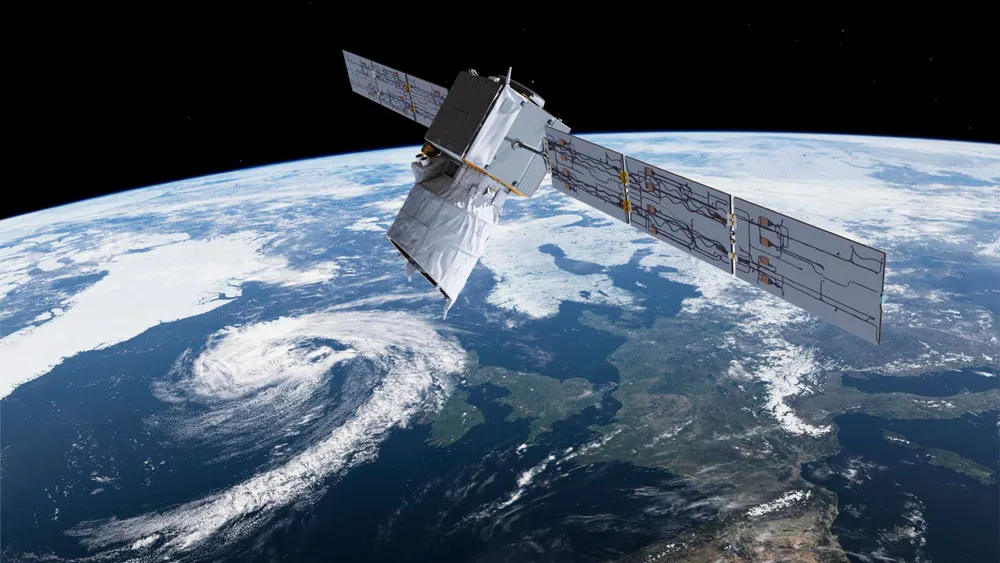

Starlink Satellite Internet
SpaceX’s Starlink provides high-speed internet to remote areas using low Earth orbit satellites, potentially connecting previously unreachable communities.
E-Rate Program (USA)
Federal program providing discounts to assist schools and libraries in obtaining affordable telecommunications and internet access.
One Laptop Per Child
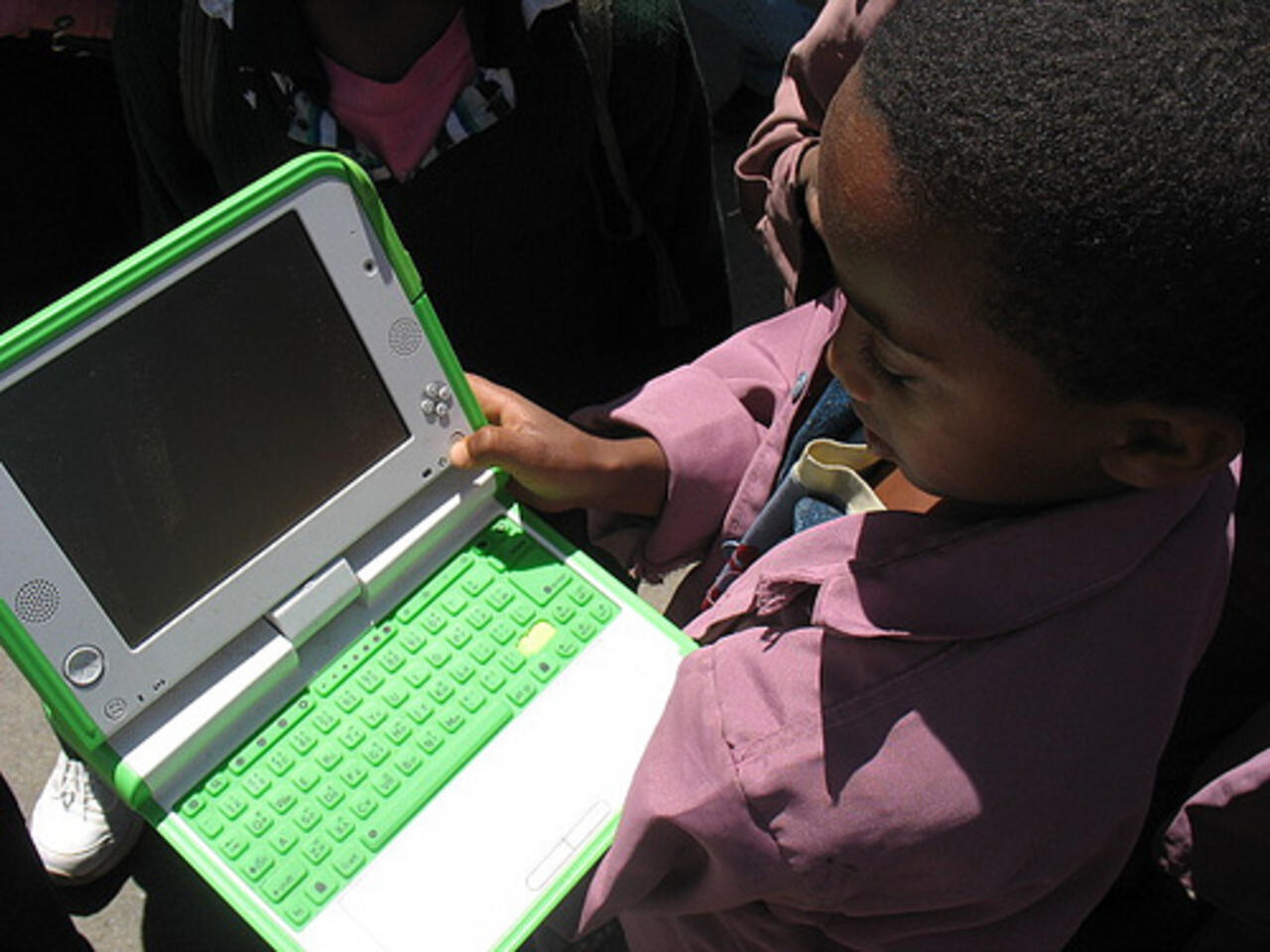

Initiative to create educational opportunities by providing low-cost, durable laptops to children in developing regions.
Community Networks
Local communities building their own internet infrastructure to serve residents in underserved areas.
Web Accessibility and the Digital Divide
🔍 Interactive Accessibility Analyzer
// Web accessibility analyzer simulation
function accessibilityAnalyzer() {
const url = prompt("Enter a website URL to analyze (simulation):", "example.com");
console.log(`\n🔍 ANALYZING: ${url}`);
console.log("Loading...");
// Simulate analysis with random results
setTimeout(() => {
// Generate simulated results
const simulatedResults = {
textSize: Math.random() > 0.3,
colorContrast: Math.random() > 0.4,
altText: Math.random() > 0.5,
keyboardNavigation: Math.random() > 0.4,
loadTime: Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 1, // 1-10 seconds
mobileResponsive: Math.random() > 0.3,
dataUsage: Math.floor(Math.random() * 5) + 1 // 1-5 MB
};
// Calculate overall score (0-100)
let score = 0;
if (simulatedResults.textSize) score += 15;
if (simulatedResults.colorContrast) score += 20;
if (simulatedResults.altText) score += 15;
if (simulatedResults.keyboardNavigation) score += 15;
if (simulatedResults.loadTime < 5) score += 15;
else if (simulatedResults.loadTime < 8) score += 7;
if (simulatedResults.mobileResponsive) score += 10;
if (simulatedResults.dataUsage < 3) score += 10;
else if (simulatedResults.dataUsage < 5) score += 5;
// Display results
console.log("\n📊 ACCESSIBILITY ANALYSIS RESULTS");
console.log("==================================");
console.log(`Overall Score: ${score}/100 ${getScoreEmoji(score)}`);
console.log("\nDetailed Results:");
console.log(`Text Size: ${simulatedResults.textSize ? '✓' : '✗'} ${simulatedResults.textSize ? 'Appropriate' : 'Needs improvement'}`);
console.log(`Color Contrast: ${simulatedResults.colorContrast ? '✓' : '✗'} ${simulatedResults.colorContrast ? 'Sufficient' : 'Insufficient'}`);
console.log(`Image Alt Text: ${simulatedResults.altText ? '✓' : '✗'} ${simulatedResults.altText ? 'Present' : 'Missing'}`);
console.log(`Keyboard Navigation: ${simulatedResults.keyboardNavigation ? '✓' : '✗'} ${simulatedResults.keyboardNavigation ? 'Supported' : 'Limited'}`);
console.log(`Page Load Time: ${simulatedResults.loadTime}s ${simulatedResults.loadTime < 5 ? '✓' : '⚠️'}`);
console.log(`Mobile Responsiveness: ${simulatedResults.mobileResponsive ? '✓' : '✗'} ${simulatedResults.mobileResponsive ? 'Fully responsive' : 'Not responsive'}`);
console.log(`Data Usage: ${simulatedResults.dataUsage}MB ${simulatedResults.dataUsage < 3 ? '✓' : '⚠️'}`);
console.log("\n💡 Digital Divide Impact:");
let impactIssues = [];
if (!simulatedResults.textSize) impactIssues.push("Users with vision impairments may struggle");
if (!simulatedResults.colorContrast) impactIssues push("Users with color blindness or visual impairments face barriers");
if (!simulatedResults.altText) impactIssues push("Screen reader users miss critical information");
if (!simulatedResults.keyboardNavigation) impactIssues push("Users without mouse/touchpad access are excluded");
if (simulatedResults.loadTime > 5) impactIssues push("Slow connections face long wait times");
if (!simulatedResults.mobileResponsive) impactIssues push("Mobile-only users struggle with navigation");
if (simulatedResults.dataUsage > 3) impactIssues push("Users with limited data plans face high costs");
if (impactIssues.length === 0) {
console.log("This site is highly accessible and helps bridge the digital divide! 🌉");
} else {
console.log("This site may contribute to the digital divide in these ways:");
impactIssues.forEach(issue => console.log(`• ${issue}`));
}
}, 2000); // Simulate 2 second analysis
}
function getScoreEmoji(score) {
if (score >= 90) return "🏆";
if (score >= 75) return "🥈";
if (score >= 60) return "🥉";
if (score >= 40) return "⚠️";
return "❌";
}
// Try it with: accessibilityAnalyzer();
Key Accessibility Factors
- Text size: Should be adjustable and readable by default
- Color contrast: Text should be easily distinguishable from backgrounds
- Alt text: Images should have text descriptions for screen readers
- Keyboard navigation: Sites should be navigable without a mouse
- Load time: Pages should load quickly on slower connections
- Mobile responsive: Content should work on all device sizes
- Data usage: Sites should minimize data requirements
📝 Key Terminology for the Exam
- Digital Divide: Gap between demographics and regions that have different levels of access to technology
- Access Divide: Disparities in physical access to technology and internet
- Usage Divide: Differences in skills and capabilities to use technology
- Digital Literacy: Ability to use digital technology effectively and appropriately
- Broadband: High-speed internet access that is always on
- Infrastructure: Physical systems needed for internet access (cables, towers, etc.)
- Universal Service: Policy aim to make telecommunications services available to all
- Digital Inclusion: Efforts to ensure all individuals can access and use technology
- Network Neutrality: Principle that all internet traffic should be treated equally
- Bandwidth: Maximum rate of data transfer across a network
- Last Mile Problem: Challenge of connecting end-user homes to the main network
- Satellite Internet: Internet access provided via communications satellites
- Community Network: Telecommunications infrastructure deployed by the community
- ICT4D: Information and Communication Technologies for Development
Study Questions
📋 Essay Practice Questions
-
Describe three dimensions of the digital divide and explain how each affects access to educational resources. Provide specific examples.
-
Compare and contrast the digital divide challenges faced in urban versus rural communities. What solutions might be effective in each context?
-
Analyze how the COVID-19 pandemic exposed and potentially exacerbated existing digital divides. Include at least three specific examples.
-
Explain how economic factors contribute to the digital divide and propose policy solutions that might address these economic barriers.
-
Discuss the ethical responsibilities of technology companies and software developers in addressing the digital divide. What specific actions could they take?
🎯 Multiple Choice Practice
- Which of the following is NOT considered a dimension of the digital divide?
- A) Access divide
- B) Usage divide
- C) Quality divide
- D) Encryption divide
- E) Participation divide
- In the United States, approximately what percentage of rural residents lack access to broadband internet?
- A) 5%
- B) 17%
- C) 28%
- D) 42%
- E) 63%
- Which of the following would be the LEAST effective solution for bridging the digital divide in remote rural areas?
- A) Satellite internet
- B) Public WiFi hotspots in town centers
- C) Mobile broadband expansion
- D) Fiber optic cable deployment
- E) Community mesh networks
- A website that requires 10MB of data to load would create the biggest barrier for users who:
- A) Are using an older computer
- B) Have a visual impairment
- C) Are on a limited mobile data plan
- D) Are not technically proficient
- E) Use a small screen device
- Which of the following best describes the concept of “digital literacy”?
- A) The ability to read digital text
- B) Knowledge of programming languages
- C) Skills needed to effectively use digital technology
- D) Access to digital devices
- E) Understanding of digital security protocols
Projects and Activities to Deepen Understanding
🗺️ Digital Divide Map
Create a visual map of your community identifying digital access points (libraries, cafes with WiFi) and areas with limited connectivity.
🔍 Accessibility Audit
Analyze a popular website for accessibility features that would help bridge the digital divide.
👨🏫 Digital Literacy Tutorial
Create a tutorial aimed at helping senior citizens or other groups learn an essential digital skill.
College Board 2018 Practice Exam MCQ Question 17
Q17 Reducing the digital divide
Which of the following actions could be used to help reduce the digital divide? I. Providing free education and training on how to use computing devices II. Providing free or low-cost computing devices to low-income individuals III. Providing networks and infrastructure to people in remote areas
- A) III only
- B) I and II only
- C) II and III only
- D) I, II, and III
Answer: D
Explanation
This option is correct. Free education and training would address digital literacy. Providing free or low-cost devices would address a lack of access to devices. Providing networks and infrastructure would address a lack of access to networks.
Questions
A government agency launches an initiative to expand high-speed internet access to rural communities by subsidizing broadband infrastructure. Despite significant investment, adoption rates remain low in many areas. Which of the following is the most likely reason for this outcome?
- A) The subsidized internet service is too expensive for many residents, preventing widespread adoption.
- B) Rural residents prefer slower internet speeds and choose not to upgrade.
- C) The program failed because rural areas do not require internet access for daily life.
- D) Expanding broadband infrastructure automatically leads to increased usage, so the data must be inaccurate.
Explanation
**Correct Answer: A** Even when broadband infrastructure is expanded, **cost remains a significant barrier** to adoption. Many low-income or rural residents may find monthly service fees too expensive, even if the infrastructure is available. Additionally, **lack of digital literacy and insufficient local demand** may contribute to low adoption rates. **Why not the others?** - **B is incorrect** because rural residents do not inherently prefer slower internet; they often lack **affordable options** or awareness of the benefits. - **C is incorrect** because internet access is crucial for many aspects of modern life, including education, healthcare, and employment. - **D is incorrect** because merely providing infrastructure **does not guarantee adoption**—affordability, education, and awareness play key roles.Question
A developing country implements a nationwide policy to bridge the digital divide by providing free internet access in public spaces, such as libraries and community centers. However, a follow-up study finds that low-income communities continue to lag behind in digital engagement. Which of the following factors best explains why the policy did not fully close the gap?
- A) Free public internet does not address barriers such as device ownership, digital literacy, and accessibility.
- B) People in low-income communities have less interest in digital tools and prefer in-person communication.
- C) The internet is now universally accessible, so any remaining gap is due to personal preference.
- D) The presence of free public Wi-Fi ensures equal access, so the study must have used flawed data collection methods.
Explanation
**Correct Answer: A** Providing free internet in public spaces is **a step in the right direction**, but it does not eliminate key barriers like: - **Device ownership:** Many individuals in low-income communities may not have personal laptops, tablets, or smartphones to effectively use the internet. - **Digital literacy:** Even with access, individuals may lack the skills to navigate online platforms for education, job applications, or essential services. - **Accessibility challenges:** Physical access to public Wi-Fi locations may be limited due to **transportation issues, time constraints, or safety concerns**. **Why not the others?** - **B is incorrect** because digital engagement is often limited by access and skills, not by personal preference. Many people in low-income communities rely on the internet for job searches, education, and financial services when given the opportunity. - **C is incorrect** because universal access has **not** been achieved; affordability and literacy remain significant barriers. - **D is incorrect** because data consistently shows that merely providing **public** internet does not eliminate disparities in digital engagement. The study’s findings align with global research on the **multifaceted nature of the digital divide**.💡 Study Tips
-
Make connections: Relate digital divide concepts to real-world situations you’ve observed in your community.
-
Use examples: For each major concept, memorize 1-2 specific examples or statistics.
-
Think interdisciplinary: Connect technology aspects to economic, social, and policy factors.
-
Stay current: The digital divide evolves, so look for recent articles or studies.
-
Consider perspectives: Think about how different stakeholders view and address the divide.
-
Visual learning: Create diagrams or mind maps connecting digital divide concepts.
-
Practice coding: Try to modify the code examples to explore different aspects of the data.
📚 Resources for Further Study
Websites:
- Pew Research Center Internet & Technology Reports
- Digital Divide Council
- National Digital Inclusion Alliance
Videos:
- TED Talks on digital inclusion
- PBS documentaries on connectivity challenges
Data Sources:
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- World Bank Digital Development
- U.S. Census Bureau American Community Survey
Interactive Resources:
- Broadband Now - Check connectivity in your area
- Digital Divide Map - FCC Maps
- Internet Health Test - Test your connection
Remember: The digital divide is not just about technology—it’s about people, opportunities, and equity. Your understanding of these issues as future technologists will shape how inclusive our digital future becomes.